What is Methanol?
What is Methanol?
Heating value
MWh/t
H2 Storage
per ton MeOH
Methanol demand/year
Mio. tons
Density at 25°C
g/cm3
Heating value
MWh/t
H2 Storage
per ton MeOH
Methanol demand/year
Mio. tons
Density at 25°C
g/cm3
benefits of Methanol
1
Liquid at Atmospheric Pressure
2
Liquid at Temperatures
-98 °C to 65 °C
3
Hydrogen carrier with 4 H2 atoms
4
Natural Substrate of microbiological
Metabolism
benefits of Methanol
1
Liquid at Atmospheric Pressure
2
Liquid at Temperatures
-98 °C to 65 °C
3
Hydrogen carrier with 4 H2 atoms
4
Natural Substrate of microbiological
Metabolism
WHAT IS METHANOL USED FOR?
WHAT IS METHANOL USED FOR?

THE FORESEEABLE MARKET DEVELOPMENT
THE FORESEEABLE MARKET DEVELOPMENT
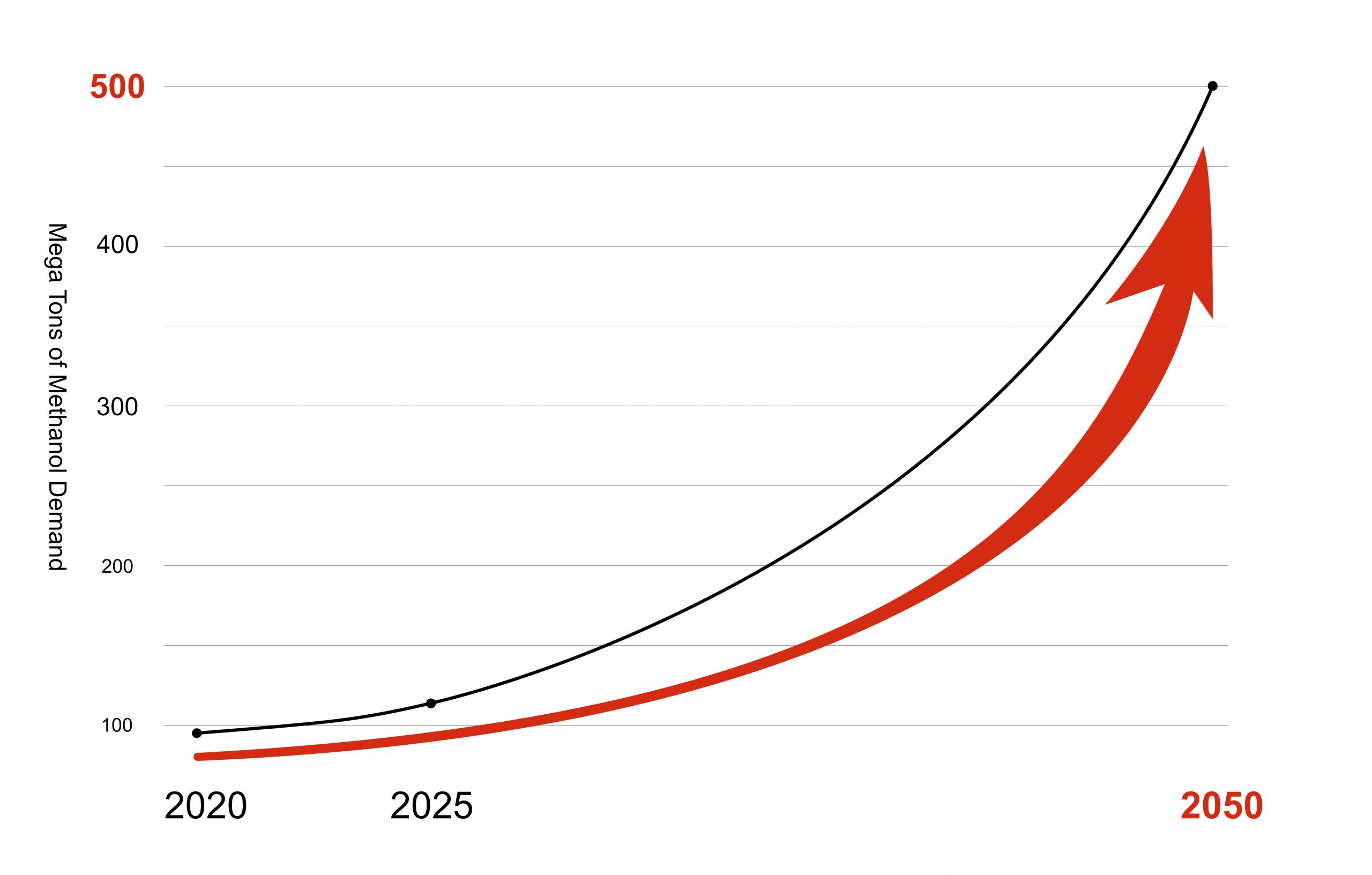
Source: International Renewable Energy Agency and Methanol Institute: “Innovation Outlook : Renewable Methanol”, January 2021
Today, fossil methanol is mainly produced from natural gas or from coal gasification. In all plants, the synthesis gas produced (carbon monoxide and hydrogen) is passed over a copper-zinc-aluminium catalyst under pressure and temperature and thus synthesised into methanol.
Global demand today is around 100 million tonnes.
Methanol can also be synthesised from the reactants carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Carbon dioxide can be captured from the air (DAC) or from point sources and thus contribute to climate protection.
The carbon is thus recycled and reused several times, avoiding additional fossil coallen fuel extraction and subsequently carbon dioxide emissions.
According to the publication of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), an e-methanol demand of 250 million tonnes is forecast by 2050 for the achievement of the Paris climate protection goals. To achieve these goals , IRENA recommends the construction of modular standardised plants.
THE METHANOL MARKET TODAY:
THE METHANOL MARKET TODAY:
Methanol (CH3OH) is a basic chemical with many uses and derivatives. Approximately 70% is used as a material. About 30% is used as an energy source.
Important derivatives are :
- Formaldehyde,
- Acetic acid, dimethyl ether (DME),
- Olefins Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE),
- Methyl methacrylate,
- Methyl chloride and methylamines.
Application in the energy sector today:
- MTBE
- Blending in petrol
- Biodiesel (FAME)
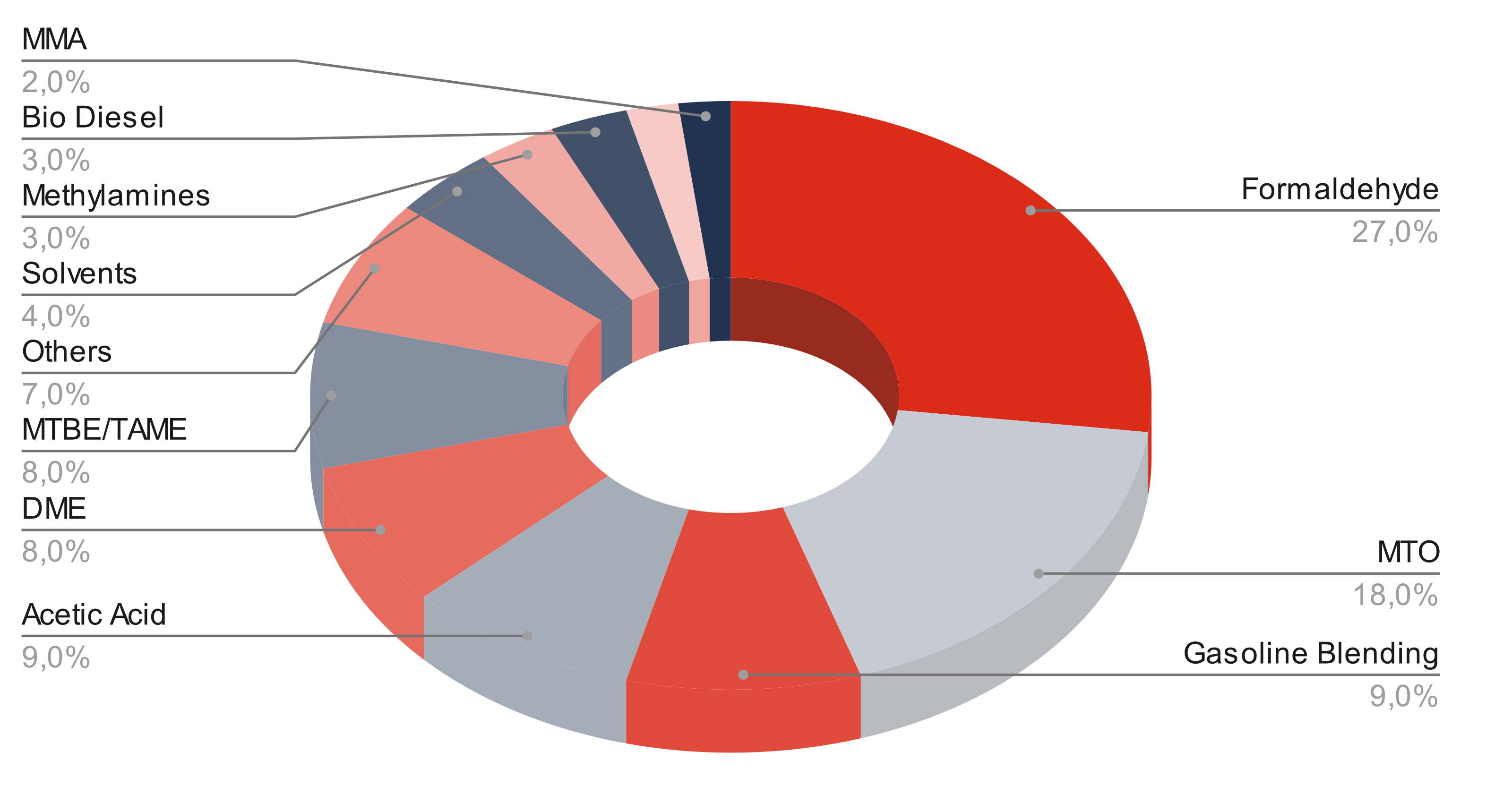
Use of methanol after end use
HOW IS OUR E-METHANOL PRODUCED?
HOW IS OUR E-METHANOL PRODUCED?
Methanol synthesis has been catalytically operated in large-scale industry since 1923.
CO2
0,04 – 100 %
From, air, flue gases and fermentation

CO2
0,04 – 100 %
From, air, flue gases and fermentation

CO2 Source
CO2 is purified from the flue gas or exhaust gas of combustion processes, biogas plants, fermtation processes of ethanol plants, steelworks, lime and cement industry in a high purity with significantly improved, biodegradable amine solutions.
Water
Electricity

Water
Electricity

ELECTROLYSIS
With the help of intermittent electrolysis, the surplus electricity is converted into H2. The conversion is open to the market with standardised electrolysis units.

Oxygen
O2
Heat
up to 80 ºC

Oxygen
O2
Heat
up to 80 ºC
METHANOL SYNTHESIS
The methanol synthesis is carried out by means of a recycle gas flow in an reactor using the catalyst.
The process conditions are adapted to those of the upstream and downstream processes and are highly thermally integrated.
The synthesis itself can be operated flexibly with a load change from min load to max load within a short time.
Methanol
CH3OH
purity of 65 %

Methanol
CH3OH
purity of 65 %
Methanol distillation
With high-capacity columns, the system overcomes typical design limitations. After distillation, the methanol achieves the globally recognised IMPCA quality.

Methanol
CH3OH
purity of 99,85 % (IMPCA)

Methanol
CH3OH
purity of 99,85 % (IMPCA)
CO2
0,04 – 100 %
From, air, flue gases and fermentation
Water
Electricity


CO2 Source
CO2 is purified from the air, flue gas or exhaust gas of combustion processes, biogas plants, fermtation processes of ethanol plants, steelworks, lime and cement industry in a high purity with significantly improved, biodegradable amine solutions.
ELECTROLYSIS
With the help of flexible electrolysis, the intermittent electricity is converted into H2 and oxygen. The conversion is open to the market with standardised electrolysis units.
METHANOL SYNTHESIS
The methanol synthesis is carried out by mean of a recycle gas flow in a reactor using the catalyst.
The process conditions are adapted to those of the upstream and downstream processes and are highly thermally integrated.
The synthesis itself can be operated flexibly with a load change from min load to max load within a short time.
Methanol distillation
With high-capacity columns, the system overcomes typical design limitations. After distillation, the methanol achieves the globally recognised IMPCA quality.

Oxygen
O2
Heat
up to 80 ºC

Methanol
CH3OH
purity of 65 %

Methanol
CH3OH
purity of 99,85 % (IMPCA)
CONTEXT E-METHANOL
Legal
Aligns with the goals of the Green Deal and the European “Fit for 55” package and climate protection goals formulated therein, in particular through the obligation to use renewable fuels (e-fuels).

Commercial
New value creation paths for industry due to increasing demand and low capacities of existing products (fuel, basic chemicals, energy and hydrogen carriers)
Society
Preservation of the environment & creation of jobs, circular economy, sustainable social development, avoidance of land consumption & biodiversity.
CONTEXT E-METHANOL

LEGAL
Aligns with the goals of the Green Deal and the European “Fit for 55” package and climate protection goals formulated therein, in particular through the obligation to use renewable fuels (e-fuels).
SOCIETY
Preservation of the environment & creation of jobs, circular economy, sustainable social development, avoidance of land consumption & biodiversity.
COMMERCIAL
New value creation paths for industry due to increasing demand and low capacities of existing products (fuel, basic chemicals, energy and hydrogen carriers)
You want to know more about Methanol?
You want to know more about Methanol?
Here you will find some useful links and tips:

